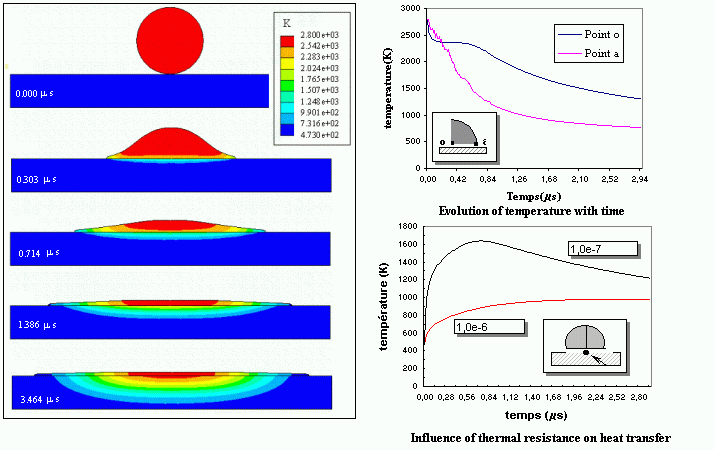
FER/Drop - Numerical modeling on the impact and the heat transfer of molten particle during the plasma spray
The transient flattening behavior of a fully molten liquid aluminum particle impinging onto a rough surface has been investigated numerically by means of a program FER/Drop developed in my Ph.D. study. The solution of the conservation equations of mass and momentum is based on Newton-Raphson and Euler implicit methods. The effect of the substrate roughness is taken into account by introducing the friction resistance at the particle-substrate interface. In particular, the Lagrangian finite element method coupled with an automatic remeshing technique allows to solve successfully the large deformation problem of liquid particle flattening with free surface.
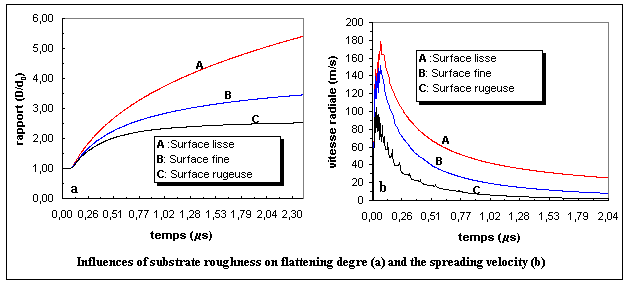
The numerical results show that the spreading process of a liquid particle is governed not only by the inertia and viscous forces but also by the frictional resistance of the substrate surface. The roughness has hence a significant influence on the spreading velocity, flattening degree, flattening time, as well as splat size and shape.
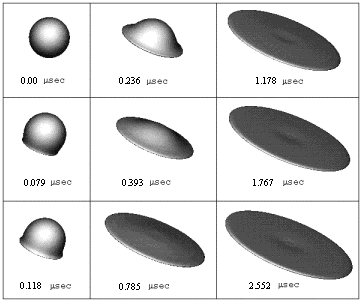
The 3D view of the spreading procedure of a molten particle during plasma spray

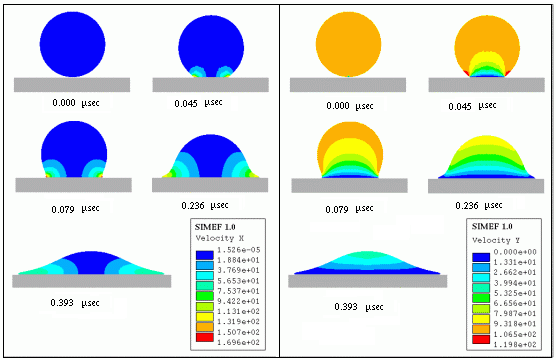
Iso-value of the velocity fields during the flattening of molten particle
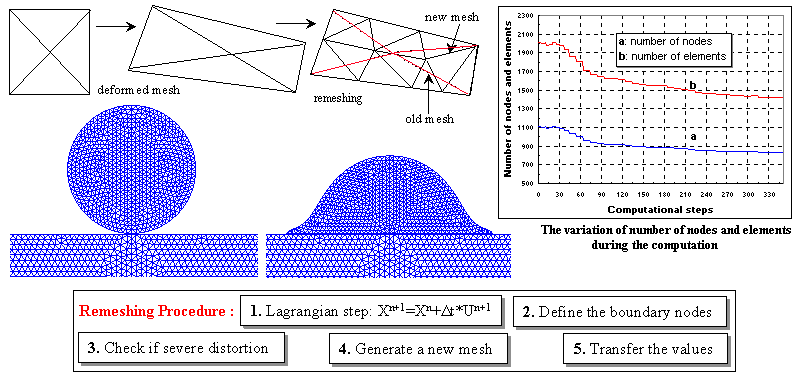
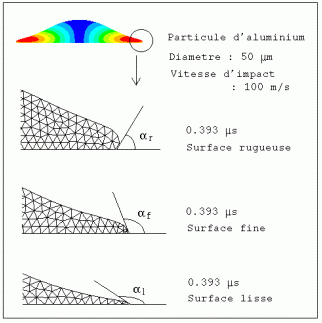
The remeshing method for modeling the large deformation of the particle
The influence of substrate roughness on the flattening of molten particle
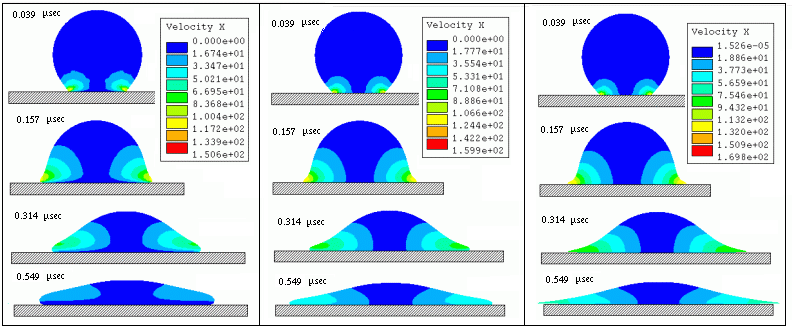
Evolution of temperature during the flattening process